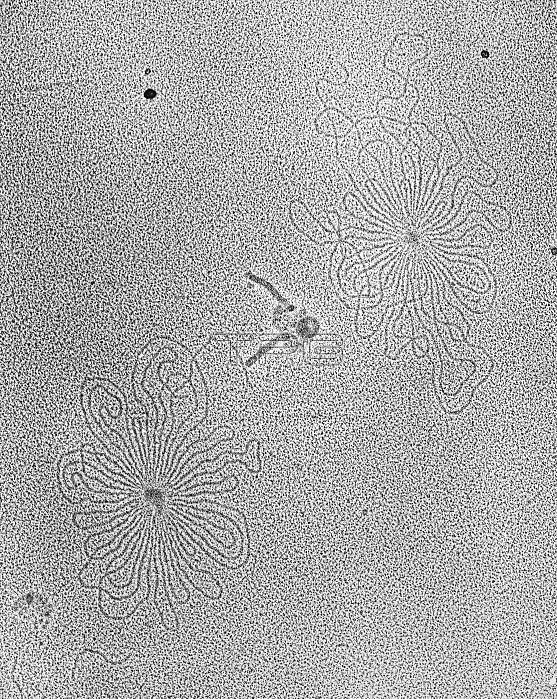
Tramnsmission Electron Microscope (TEM) of DNA of two lamda wild type bacteriophages. The ghosts of the phages are also seen in the center of the field. Enterobacteria phage (lambda phage, coliphage) is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli (E. coli). The wild type of this virus has a temperate lifecycle that allows it to either reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny or enter into a lytic phase (during which it kills and lyses the cell to produce offspring); mutant strains are unable to lysogenize cells- instead they grow and enter the lytic cycle after superinfecting an already lysogenized cell. The phage particle consists of a head (capsid), a tail, and tail fibers. The head contains the phage's double-strand linear DNA genome. During infection, the phage particle recognizes and binds to its host, E. coli, causing DNA in the head of the phage to be ejected through the tail into the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell. Magnification: 100,000x.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22219981
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
Restriction:
Editorial use only

 Loading
Loading