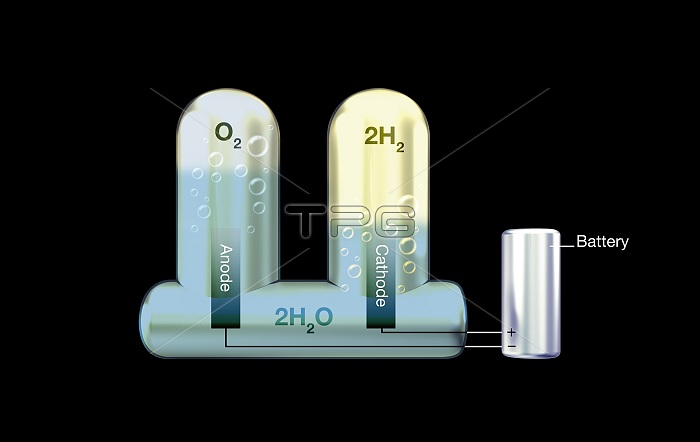
Electrolysis of water, illustration. Electrolysis is the use of an electrical current to decompose a chemical, in this case water. Reactions at the two electrodes (anode and cathode) are powered by the electric current from the battery (right). The electric current splits the water (H2O) into its elemental parts. Oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2) gas bubbles are evolved at the anode (left electrode) and cathode (right electrode) respectively. As water molecules consist of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, twice as much hydrogen as oxygen is trapped in the test tubes. First carried out in 1800, this is a key science experiment taught in schools. For this image with different background and with and without labels, see C046/8153 to C046/8159.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP24755268
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading