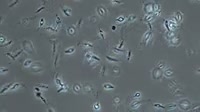
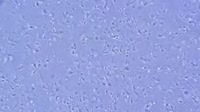
Leishmania aethiopica parasites, light microscopy. L. aethiopica is a protozoan that causes the tropical disease leishmaniasis, which is transmitted by the bites of infected sandflies. These are the motile promastigote forms of the parasite, which are injected into the blood by the sandfly's bite. Once inside the bloodstream they invade or are engulfed by phagocytic macrophage white blood cells, but are not destroyed, and instead hide from the immune system inside the cells. Thus hidden, the transform into the amastigote stage and reproduce, bursting from the cell to infect others. The amastigotes are then picked up the next time a sandfly bites and drinks blood, turn into the promastigote form, and the cycle continues. Leishmaniasis caused by L. aethiopica causes skin ulcers, typically at and around the bite site. The disease is typically self-limiting and heals over time, but persistent cases can be treated with pentavalent antimony drugs, or antibiotics such as paromomycin. Filmed with phase contrast illumination.
Details
WebID:
C01809061
Clip Type:
RM
Super High Res Size:
1920X1080
Duration:
00:00:46.000
Format:
QuickTime
Bit Rate:
25 fps
Available:
download
Comp:
200X112 (0.00 M)
Model Release:
NO
Property Release
NO









 Loading
Loading