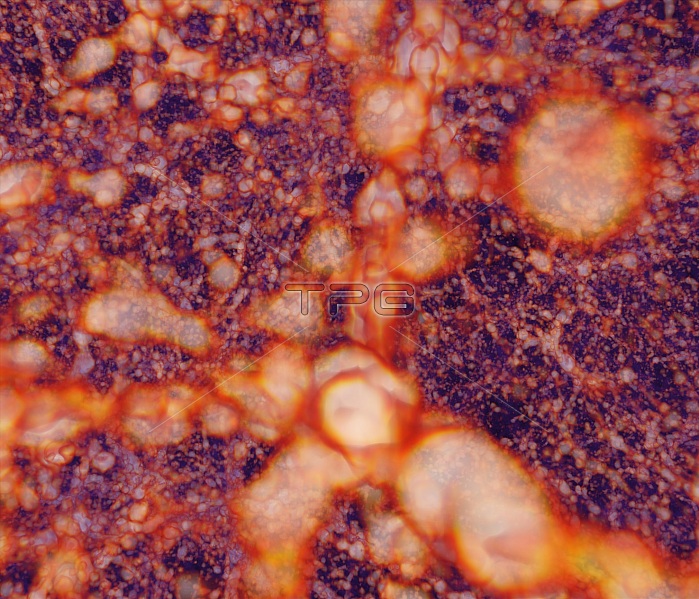
This image shows a large simulation of the distribution of matter in the Universe, the so-called cosmic web, which evolved under the influence of dark energy. The orange and white structures depict matter concentrations, where galaxies and clusters of galaxies are forming. The simulation was run with 1.1 trillion particles on Mira, the Blue Gene/Q system at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility, using HAAC (Hardware/Hybrid Accelerated Cosmology Code), a new simulation framework developed to overcome the challenges posed by future supercomputing architectures. In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy which is hypothesized to permeate all of space, tending to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Mira is a petascale Blue Gene/Q supercomputer. As of June 2013, it is listed on TOP500 as the fifth-fastest supercomputer in the world
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22302269
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:

 Loading
Loading