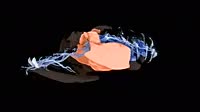
Solubility of oleic acid, a fatty acids. Fatty acids are high molecular weight carboxylic acids with a large aliphatic carbon chain dominating their molecular structure. This carbon chain is non-polar and as a result, fatty acids do not readily mix with polar water molecules. This is evident here, as the mixture forms two separate layers with visible surface tension between them. It floats on the water layer as it is less dense. Oleic acid is a mono-unsaturated acid with the formula CH3(CH2)7CHCH(CH2)7COOH. It is common in vegetable and animal fats, as a triglyceride, and is the most abundant fatty acid in human fat tissue.
Details
WebID:
C01787360
Clip Type:
RM
Super High Res Size:
1920X1080
Duration:
00:00:28.000
Format:
QuickTime
Bit Rate:
25 fps
Available:
download
Comp:
200X112 (0.00 M)
Model Release:
NO
Property Release
No












 Loading
Loading